FORUM DI EPISTEME
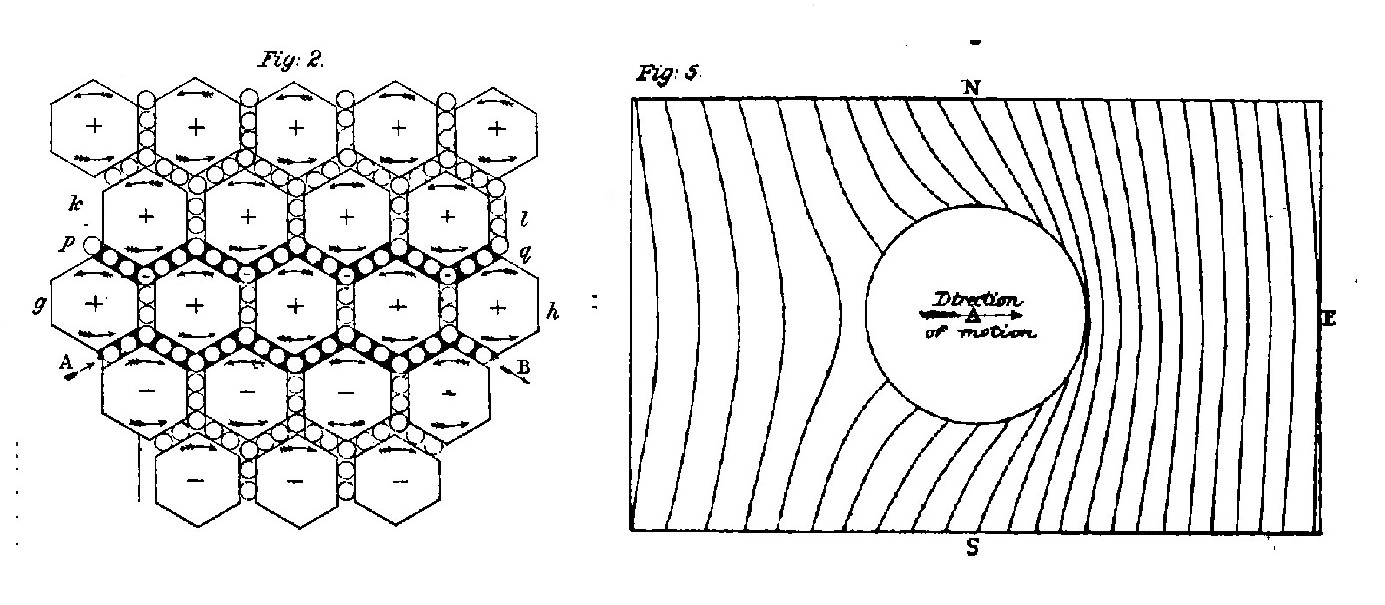 Maxwell's
sea of molecular vortices 1861,
Maxwell's
sea of molecular vortices 1861,
the inspiration for "The Double Helix Theory of
the Magnetic Field"
_____________________________________________________________
4 - Frederick
David Tombe
sirius184@hotmail.com
- - - - -
The following 1st July 2010 revision of "The Double Helix
Theory of the Magnetic Field" summarizes all the most important
issues that have been covered in the various revisions since the original
paper of 15th February 2006.
Abstract.
In 1856, Wilhelm Eduard Weber and Rudolf Kohlrausch
performed an experiment with a Leyden Jar which
showed that the ratio of the quantity of electricity
when measured statically, to the same quantity of
electricity when measured electrodynamically, is numerically
equal to the directly measured speed of light. In 1861,
in his paper entitled ‘On Physical Lines of Force’, James
Clerk-Maxwell equated the above ratio with the ratio of
the dielectric constant to the magnetic permeability.
In the same paper, Maxwell modeled Faraday’s magnetic lines
of force using a sea of molecular vortices that were composed
partly of aether and partly of ordinary matter. He linked
the dielectric constant to the transverse elasticity of this
vortex sea, and he linked the magnetic permeability to the
density. Since Newton’s equation for the speed of sound involves
the ratio of the transverse elasticity to the density,
Maxwell was able to use Weber’s constant to show that light
is a wave in the same medium that is the cause of electric and
magnetic phenomena. It will now be suggested that Maxwell’s
molecular vortices are more accurately represented with rotating
electron-positron dipoles that are aligned in a double helix
fashion with their mutual rotation axes tracing out the magnetic
lines of force.
May 2016
- A new version of the previous paper:
Abstract.
The historical linkage between optics
and electromagnetism can be traced back to a paper published
in the year 1856 by Wilhelm Eduard Weber and Rudolf Kohlrausch.
By discharging a Leyden Jar (a capacitor), they showed that the
ratio of the electromagnetic and electrostatic units of charge is
numerically equal to the directly measured speed of light. Weber
interpreted this result as meaning that the speed of light is a kind
of escape velocity for electricity in motion, such as would enable
the associated magnetic force to overcome the electrostatic force.
An alternative interpretation was advanced a few years later
by James Clerk-Maxwell who connected the result to the elasticity
in an all pervading solid medium that serves as the carrier of light
waves. As a consequence, he concluded that light waves are electromagnetic
undulations. These two perspectives can be reconciled by linking
the speed of light to the circumferential speed of the molecular
vortices which Maxwell believed to be the constituent particles
of the solid luminiferous medium. If we consider these molecular vortices
to be tiny electric current circulations, magnetic repulsion can then
be explained in terms of centrifugal force. And if these molecular
vortices should take the form of an electron and a positron in mutual
orbit, we can then also explain magnetic attraction in terms of the more
fundamental electrostatic force being channeled through space along
double helix chains that constitute magnetic lines of force.
* * * * *
B - Gravitation,
Electrostatics, and
the Electron-Positron Aether
(Ether)
(Based
on the 1982 paper by David Tombe, entitled
"Electrogravitomagnetism")
[22nd August
2008 - This paper has been
totally withdrawn, for the reason that it centres around a theory
which attempts to rationalize inertial mass as being
related to the sum of the "modulus" of the electric
charge in a body. More recently, I have been working on
a different principle as explained in the paper at N2 entitled
"Negative Mass and the Gravity Sink". The
ideas contained in this paper concerning inertial mass were
only peripheral to the main theme regarding an electron-positron
luminiferous medium. These ideas concerning inertial mass
have now been superseded by a new theory which involves absolute
values as opposed to 'modulus' values of charge
.
(We maintain nevertheless
a copy of the paper for history's sake.)
3rd November 2011
- A comment from the author. There is really
no important need to withdraw this paper. I am once
again of the opinion, as was stated in the paper, that
mass is a cumulative quantity based on all the particles
in a body. I can add that it is widely believed, due to a
common error in the secondary literature, that Maxwell conceived
of displacement current in connection with the electric capacitor
circuit. In actual fact, Maxwell's original paper of 1861, part
III, indicates that he did not conceive of displacement
current in connection with the electric capacitor circuit. This
paper, based on research done in 1982, perpetrates that common
error, and the author has corrected it in future articles.
The author also now notes that the displacement current term as
is used in the derivation of the electromagnetic wave equation,
should be magnetization based, and not linear polarization based.
In other words, it should be a rotatory effect and not a linear effect.]
23rd January 2011 - This
paper has been fully revised, here is in red a comment
from the author (we maintain previous comments again
for history's sake).
- This article
was written in 2003 based on original material from
1982, without any revision of the core ideas. Research was
commenced again in 2004. As a result of seven further years
of investigation, comments have now been added in
red by the author, in order to draw attention to the
revised views in the light of the more recent research. The first
issue concerns the title itself. The electron-positron sea is
not the aether as such. Positrons are aether sources and electrons
are aether sinks. The electrons and positrons are paired in
mutual orbits to form rotating dipoles, and as such the electron-positron
medium for the propagation of light is actually a sea of tiny dipolar
aether whirlpools.
E - Gravity Reversal
and Atomic Bonding
(A Theory of Mutually Attracting Sinks)
[Note of the Editor: As far
as the following assertion
is concerne d:
«
the Earth's magnetic
field is explained by virtue
of the fact that the Earth is a rotating
negatively charged object»
, the reader could
be interested even in the paper presented
in next point 8.]
(The
Epicycle Theory of the Atom)
(New
revised version: 5th August 2008)
I - Charge, Spin,
and 'Charge to Mass'
Ratio
(A Unified
Theory of Gravity and Electricity)
22nd August 2008: This paper has
been
totally withdrawn
(together with
paper B)
, for
the reason that it centres around a
theory which attempts to rationalize
inertial mass as being related to the
sum of the "modulus" of the electric
charge in a body. More recently, I have been
working on a different principle as explained
in the paper at N2 entitled "Negative Mass and
the Gravity Sink".
The ideas contained in this paper concerning
inertial mass were only peripheral
to the main theme regarding an electron-positron
luminiferous medium. These ideas concerning
inertial mass have now been superseded
by a new theory which involves absolute values
as opposed to 'modulus' values of charge,
and the theories concerning
centrifugal force and Coriolis force contained
within this paper have been expanded upon in the
paper at Q2 entitled "The Cause of Centrifugal Force"
.
(We maintain nevertheless a
copy of the paper for history's sake.)
(New revised version: 5th August 2008)
L -
The
Aether and the Electric Sea
(The
Link between Gravity and Electromagnetism)
(New
revised version: 18th February 2009)
(New
revised version: 5th March 2009)
New
revised version: 18th March 2009
( "The
amendment changed a paragraph in the section
about inertia")
(New
revised version of L: 2nd June 2009
"Another
section mentioning inertia was removed". We
maintain nevertheless a copy of the
previous paper for history's sake.)
(New
revised version of U': 2nd June 2009
"This
was a major amendment based on the realization
that the Coriolis force is a real transverse
force that arises in connection with the
conservation of angular momentum". We maintain nevertheless
a copy of the previous paper for history's
sake.)
Y - The Four Kinds of Electric
Charge
(A vitreous electricity explanation for infinite
supplies of electric charge)
(New revised version: 24th September 2008)
(New
revised version: 14th December 2008)
(New
revised version: 2nd June 2009
"A
general re-wording without any major change in
the content".)
A2' - Bernoulli's
Principle and the Theory of Flight
(New revised version
of A2: 2nd June 2009
"This
was a major re-write with an increased emphasis
on the role of the centrifugal force in
the air molecules". We maintain nevertheless
a copy of the previous paper for history's
sake.)
(New revised version: 18th May 2008)
(New
revised version: 18th February 2009)
H2 - Bernoulli's Principle
and the AC Transformer
(New
revised version: 18th May 2008)
October 2016 - A new version of the previous
paper (this new version disregards matters to do with capacitance
as they are a red herring to the main issue: that charge is something
that must flow net into the circuit from the power
source; the idea is that charge is the pressure in an electric fluid
and that Bernoulli's principle in conjunction with conservation of
power is the governing feature in a transformer circuit; the older version
side-tracks too much to the subject of capacitance, and it doesn't sufficiently
emphasize the fact that charge must enter net as like pressurized water
into the water supply network):
Abstract.
The AC transformer is a transducer
which converts between potential energy and kinetic energy.
A step-up transformer increases the voltage and decreases
the current while a step-down transformer does the opposite. Despite
the low current, streaks of lightning arc out from high voltage
cross country power cables when earthed objects get too close.
The physical nature of voltage will now be examined.
N2 - Negative Mass and
the Gravity Sink
O2 - The General Convective Force
(A General Survey of the Coriolis force and the Centrifugal
force)
(New
revised version: 9th June 2008)
(New
revised version: 19th August 2008
)
P2 -
Centrifugal Force in the Electric
Circuit
(New
revised version: 28th December 2008:
"The
focus was in amending the section on EM induction
in relation to Coriolis Force",
see T2 and T2')
(New
revised version: 29th January 2009)
New
revised version: 18th March 2009
("The wording in the centrifugal
force section was improved to emphasize
the extrapolation of the general principle of
centrifugal force to the four body problem
in which two closed orbital systems sit side by side,
and therefore must repel each other
")
P2' -
Centrifugal Force in the Electric
Circuit
(New
revised version of P2: 2nd June 2009
"This revision goes
into much more detail on the role of the
Coriolis force in the induction of current
in a wire that is moving through a magnetic
field". We maintain nevertheless a copy of the previous
paper for history's sake.)
(New
revised version: 19th August 2008
)
(New
revised version: 7th December 2008
)
(New
revised version: 5th March 2009)
Q2' - The Cause of Centrifugal Force
(New revised version
of Q2: 2nd June 2009
"This
was a major re-write based on the realization
that the inverse cube law points to a dipole
field". We maintain nevertheless a copy
of the previous paper for history's sake.)
(New
revised version: 28th August 2008
)
(New
revised version: 14th December 2008)
S2 - The Coriolis Force and the Screw
* 30.XI.2011: This paper has now
been withdrawn, but you can still read it with an author's remark.
T2 -
Areal Velocity, Coriolis
Force, and Vorticity
T2' -
The Cause of Coriolis
Force
(New
revised version of T2: 28th December 2008)
"T2'
is a major amendment. I've taken all the contents
into what is effectively a new paper". We
maintain nevertheless a copy of the previous
paper for history's sake.
( New
revised version: 5th March 2009)
T2'' -
The Cause of Coriolis Force
(New
revised version of T2': 2nd June 2009)
"This
was a major re-write based on a clearer division
between transverse Coriolis force and axial Coriolis
force"
. We maintain nevertheless a copy of the previous
paper for history's sake.
U2 -
Displacement Current
(New
revised version: 14th December 2008)
V2 - Displacement
Current 2
(New
revised version: 18th February 2009)
Y2 - Wave/Particle Duality in Electromagnetic
Radiation
Z2 -
Wave/Particle Duality
in Cathode Rays
A3 -
Cathode Rays, Gravity, and Electromagnetic
Radiation
(New
revised version: 14th December 2008)
B3 -
Tangential Force –
The Equilibrium Shifter
(New
revised version: 29th January 2009)
New
revised version: 18th March 2009 ("
Appendix B was removed as it was a
bit hard to read, and out of context, and
it will be the subject of a separate paper some time
in the future ")
B3' -
Lenz's Law
(New
revised version of B3: 5th November 2009
This
is a major re-write of the previous paper,
we maintain nevertheless a copy of the older one for
history's sake.)
C3 - The Key
that Winds up the Universe
New
revised version: 18th March 2009 ("
Large, somewhat confusing sections
on 'inertia' were removed. A new paper on inertia
will be written some time in the future")
D3
-
Electromagnetism
and the Rolling Wheel
E3 - The Superimposition of
Radiation and Gravity
New
revised version: 5th March 2009
F3 - The Rotationally Elastic Sponge
G3 - Kepler's Law of Areal Velocity
in Cyclones
H3 -
Inertia and the Electric Sea
I3 -
The Coriolis Force is a System of Accountancy
for Real Forces
J3 -
The Physical Nature of the
Coriolis Force
Un
nuovo lavoro, febbraio 2010 - A new paper, February
2010:
K3 - Maxwell's
Sea of Molecular Vortices
L3 -
Magnetic Repulsion and Centrifugal Force
(April 2010)
M3 - The Electric Rings of Force that cause the
Tides
(September
2010)
N3 - The Coriolis Force
and the Aether (The Compound Centrifugal Force)
(December 2010)
Abstract.
The Coriolis force is induced by a compound motion
involving two independent yet physically connected
motions, one of which is linear and the other which
must be of a rotatory nature. In a paper which he wrote
in 1835, French scientist Gaspard-Gustave Coriolis referred
to it as the "compound centrifugal force ". Just like
centrifugal force, it acts to deflect an element perpendicularly
to its path of motion, but its mathematical expression
is exactly twice that of the simple centrifugal force.
It is commonly associated with atmospheric cyclones, but it
can also be observed deflecting the effect of gravity on a comet,
reversing a rotating rattleback (Celtic stone), preventing
a pivoted spinning gyroscope from toppling under the force of gravity,
and driving an electric current in a wire that is moving perpendicularly
to a magnetic field. The origins of the Coriolis force will now
be traced to differential centrifugal pressure and differential
vorticity in the dense background sea of tiny aether vortices
which serves as the medium for the propagation of light.
Abstract.
The
rattleback (Celtic Stone) is the most mysterious
phenomenon in classical mechanics. It reverses its
angular momentum by inducing a Coriolis pressure
from the dense background sea of rotating electron-positron
dipoles which is the medium for the propagation of light.
P3 - The Centrifugal Force
Paradox
(April 2011)
Abstract.
It
is commonly taught nowadays that centrifugal force
doesn't exist, except as a fictitious force that
is only observable from a rotating frame of reference.
This belief is based on Newton's law of inertia which
states that a body undergoing straight line motion at
constant speed experiences no net force, and that curved
path motion involves only a centripetal force. However,
if we split the net zero force of straight line constant
speed motion into polar components, we find that one of these
is a centrifugal force component which can physically react
with constraints, hence revealing an underlying pressure associated
with inertia. Further evidence that centrifugal force is a
real physical force arises when inertial pressure becomes asymmetrical,
as happens in a radial gravitational field or in a solenoidal
magnetic field.
Q3 - Physical Lines of Force
in the Aether
(April
2011)
Abstract.
In
the nineteenth century, James Clerk-Maxwell was
unable to explain the linkage between gravity and electromagnetism.
He realized that gravitational lines of force
must involve a pressure, as is the case with magnetic
lines of force when they are involved in mutual repulsion.
He also realized that the pressure in the magnetic lines
of force acts laterally due to centrifugal force in a sea
of molecular vortices, but he couldn't seem to similarly
explain the pressure in the gravitational lines of force
[1]. It will now be suggested that gravitational lines of force
are actually lines of tension, and that Maxwell's molecular vortices
are dielectric in nature. The linear polarization of these dipolar
vortices, caused by the gravitational field, will increase the
centrifugal pressure which is exerted laterally, and this pressure
will result in a repulsive force in competition with the attractive
force. The attractive force, being a monopole field, will obey
the inverse square law, whereas the repulsive force, being a dipole
field, will obey the inverse cube law. Hence if the charge of an object
increases, the inverse cube law relationship for the surrounding
repulsive force field will lead to a reversal threshold, where
it will dominate over the attractive force. The charge can increase
electrostatically or because of inertia. In the latter case,
the repulsive force field is the large scale centrifugal force.
R3 - Anti-Gravity and the Flying Saucer
(May 2011)
(New amended
version: 21.XI.2011)
Abstract.
There
is only one anti-gravity force, and that is positive
electric charge. Positive charge is the centrifugally
directed pressurized aether which emerges from the sources
which we understand as positively charged particles.
A particular geometrical arrangement of the positive particles
of the luminiferous medium is sought, such that it will
push a flying saucer upwards against the gravitational
field.
S3 - Centrifugal Force Denial
(June
2011)
Abstract.
When
a mooring line needs to be cast from ship to shore
over a lengthy distance, this can be accomplished by
utilizing the concept of centrifugal potential energy.
Swinging the weight in circular motion in a vertical plane,
and building it up to a high angular speed is a means of
storing up pressure. The weight can then be released underarm,
resulting in a projectile with kinetic energy corresponding
to the stored centrifugal potential energy. We can of course
choose to deny the existence of this centrifugal pressure
and explain the phenomenon on the grounds that we are merely
witnessing the tendency of an object to move in a straight line
in the absence of an applied force. But we can only indulge in
this denial in the absence of a radial or a solenoidal field,
and such fields exist everywhere. It will now be shown how centrifugal
force corresponds to positive electric charge, kinetic energy,
and inertia, and how a magnetic field is a particular manifestation
of inertia.
T3 - Bernoulli's Theorem and the Principle of Flight
Abstract.
When
an aeroplane moves horizontally through the air,
the air pressure below the wings is greater than the air
pressure above the wings. This causes a force to act vertically
upwards on the aeroplane, at right angles to its direction
of motion. Likewise when an electric current flows through
a wire in a magnetic field, a differential pressure is exerted
on either side of the wire, causing a force to act at right angles
to the wire. In the former case the pressure arises from the
centrifugal force that is being exerted by the air molecules, whereas
in the latter case the pressure arises from the centrifugal force
that is being exerted by the tiny molecular vortices that form the
medium for the propagation of light.
U3 - Centrifugal
Force
From F.D.
Tombe: I decided to do a paper dedicated exclusively
to 'centrifugal force'. Other papers that I have written
incorporate my views on centrifugal force, but this paper
is designed to directly counter the official mainstream
point of view on centrifugal force.
Abstract.
It is nowadays taught that centrifugal
force is a fictitious force that can only be observed from
a rotating frame of reference. This teaching is based
on the argument that when no inward centripetal
force is acting, a particle will proceed in its straight
line inertial path. In situations where the physical effects
of centrifugal force are detected, this is dismissed as being
merely the effects of inertia. Polar coordinates relative to
a point origin expose a centrifugal force acting on a particle
that is moving in a straight line, but this centrifugal force tends
to be masked from view by virtue of the fact that the radial position
vector is rotating. This article will examine ways to expose
the physical reality of the centrifugal force.
V3 - Double Centrifugal Force
Abstract.
This
article examines a situation in which two completely
separate centrifugal forces are acting within a single
rotating system. One centrifugal force relates to
the rotation axis of the rotating system, while the other
centrifugal force relates to the centre of the Earth and
the horizontal transverse speeds within the rotating system.
The latter has the power to cause an object to rise vertically
in defiance of gravity.
Z3 - The Coriolis Force (The Compound Centrifugal
Force)
Abstract.
The
Coriolis force is generally associated with the
Earth's rotation, although it can arise in connection
with any kind of rotation. In a paper which he wrote
in 1835, French scientist Gaspard-Gustave Coriolis referred
to it as the "compound centrifugal force", and that is exactly
what it is. It is a compound inertial force which results when
a compound motion causes two opposing centrifugal pressures
to press differentially on either side of an object. When
an object moves through the medium for the propagation of
light, this induces an inertial pressure around the object which
is manifested as kinetic energy. When this inertial pressure
is asymmetrical, such as is the case in a radial or in a solenoidal
field, the asymmetry is manifested as an inertial force. In meteorology,
the asymmetry which leads to the Coriolis force being induced
in cyclones is complicated by the fact that there are two centres
of rotation involved, and hence we are dealing with a double Coriolis
force. With the double Coriolis force in meteorology, there is the
rotation that is centred on the Earth, and there is also the rotation
that is centred on the cyclone itself.
A4 - Maxwell's Original Equations
From
the Introduction:
Although Maxwell's
most important equations had already appeared throughout
his seminal paper entitled "On Physical Lines of Force",
which was written in 1861 in Great Britain, it was not
until 1864 that Maxwell created a distinct listing of eight
equations in a section entitled "General Equations of the
Electromagnetic Field" in his follow up paper entitled
"A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field". While Maxwell
refers to twenty equations at the end of this section, there
are in fact only eight equations as such. Maxwell arrives
at the figure of twenty because he splits six of these equations
into their three Cartesian components. Maxwell's eight
original equations will be discussed in depth in individual
sections throughout this paper.
B4 - Electric Current (Cable Telegraphy and Wireless Telegraphy)
Abstract.
Poynting's theorem applies to wireless telegraphy
as well as to electric circuits and cable telegraphy. We
will therefore seek to establish the commonality between these
three phenomena.
C4 - Newton's Cradle and the Transmission Line
Abstract.
Two
electric currents flowing in opposite directions along
the same wire in a transmission line appear to pass right
through each other. We therefore require a theory of electric
current that can account for this, while at the same time
maintaining consistency with Ampère's circuital law.
D4 -
The Distortion of Maxwell's Equations
Abstract.
James
Clerk-Maxwell is credited with having brought electricity,
magnetism, and optical phenomena, together into one
unified theory. The details of what exactly he did were
however seriously distorted in twentieth century physics
textbooks. Maxwell is most famous in connection with a
set of equations which bear his name, but these equations have
been totally removed from the physical context within which
Maxwell was working, and outside of that physical context the
full meaning of these equations is lost. Maxwell was working within
the context of a sea of tiny aethereal vortices pressing against
each other with centrifugal force. The centrifugal force bit was
crucial for explaining magnetic repulsion, yet both centrifugal
force and aether are stringently denied by modern physicists who nevertheless
continue to hail Maxwell for the equations that he derived by using
these very concepts which they deny. This irony seems to be explained
at least in part because they think that the equations can be re-derived
using Einstein's special theory of relativity. Such an erroneous
belief stems from the fact that one of the most important of Maxwell's
equations has been wrongly credited to Lorentz and referred to as
the Lorentz force law and treated as ‘supplementary’ to Maxwell's equations.
Einstein, being ignorant of Maxwell's original equations and the fact
that they contained the Lorentz force law, hence wrongly believed that
the equations contained no convective term, and so he made the erroneous
conclusion that Maxwell's equations mean that the speed of light must
be frame independent in contradiction of classical principles of vector
addition of velocities. This erroneous conclusion led Einstein to his
special theory of relativity in 1905, and it subsequently led to the
erroneous belief amongst both relativists and many anti-relativists,
that Einstein's special theory of relativity follows naturally from
Maxwell's theory, when in fact Maxwell and Einstein were not even remotely
working along the same lines.
E4
-
The Two Kinds of Electric Charge
Abstract.
In
an earlier article, it was explained how there are
four kinds of electric charge. There are in fact only two
kinds of electric charge. The earlier article created four
kinds of charge by identifying both a simple and a compound
version for each of positive and negative charge. Simple charge
was based on the tension and pressure associated with pure
aether flow, in and out of negative and positive particles, while
compound charge was about the intermediary effect of the electron-positron
dipoles that fill the space between charged bodies. A charged
body linearly polarizes the surrounding electron-positron sea
and this causes a centrifugal repulsive force to act laterally
from the field lines. It will be explained how two negative charges
may either attract or repel depending on the strength of the
charge, and hence explaining the link between gravity and electrostatics.
F4 - Electric Current and Dielectrics
Abstract.
A dielectric medium
impedes electric current due to the fact that the constituent
dipoles become linearly polarized and induce a back EMF.
A capacitor in an electric circuit utilizes the principle that
a dielectric gap in the conducting material causes impedance and
acts like a dam, hence enabling electricity to be stored in
the circuit. This same dielectric effect can also be used in transmission
lines. We will now examine the discharging process in a capacitor
with reference to a transmission line pulse, while taking care
not to ignore Ampère's Circuital Law. A general principle will
be proposed in which an electric circulation commences at the
contact point of discharge, and that this circulation expands in two
opposite directions, eating its way backwards into the original charged
zone while simultaneously extending forwards beyond it, such as to
create a region that is twice as long as the original zone, but exhibiting
a lesser degree of linear polarization.
G4 - The Centrifugal Force and the Coriolis Force
Abstract.
In 1835, French scientist
Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis wrote a paper in which
he mathematically derived equations of motion for rotating
coordinate systems [1]. In this paper he drew attention to
two categories of supplementary forces. Coriolis referred
to these forces in the plural. The forces in the first category
were the ordinary centrifugal forces, while the forces in
the second category were described as being equal to twice the
product of the angular velocity of the mobile plane, taken with
respect to the relative momentum as projected unto that plane. By
analogy with the mathematical formula for the ordinary centrifugal
forces, Coriolis called this second category of supplementary
forces "The compound centrifugal forces". This paper aims
to establish the fundamental physical cause behind centrifugal force
as well as its connection with the medium for the propagation of
light.
[1] Gaspard-Gustave
Coriolis, «Sur les équations du mouvement relatif
des systèmes de corps», J. de L'Ecole Royale Polytechnique,
24th cahier, p. 142, 1835.
H4 - The Centrifugal Force Argument
Abstract.
The modern teaching is
that centrifugal force only exists in a rotating frame
of reference and that the only force that acts in an inertial
frame of reference when a body undergoes circular motion
is an inward acting centripetal force. On the contrary however
it is here proposed that a rotating frame of reference, rather
than creating an inertial centrifugal force, actually masks
a hithertofore unrecognized inertial centripetal force. When
the books are correctly balanced, it will be demonstrated that
centrifugal force is a real force, closely related to kinetic
energy, and observable in any frame of reference.
I4 - The Speed of Light
Abstract.
The aether
(or electricity) is a fluid-like substance that is
the stuff of all matter and space, and it flows constantly between
positive and negative particles, with particles being merely
aether sources and aether sinks. Space is densely packed
with aether sinks (electrons) and aether sources (positrons). These
electrons and positrons are paired into tiny dipoles. Within
each dipole, the electron and the positron will undergo a mutual
circular orbit. In the steady state, these tiny dipolar aether
vortices will align with their neighbours according to two superimposed
principles. Their rotation axes will mutually align and trace out
solenoidal lines around a magnetic dipole. The resulting electron-positron
double helix that winds its way around each such line is what causes
the electrostatic tension that makes it into a 'magnetic line of
force'. When large scale aether flow, constituting either an externally
applied gravitational field or an electric current (electric field),
is superimposed, the tiny vortices will become linearly polarized.
This will result in a 'couple force' acting on the tiny vortices
which will cause them to precess such that their precessional axes
will be aligned with the externally applied field lines. Centrifugal
pressure therefore acts at right angles to both magnetic and electric
lines of force. In the dynamic state the alignment of the dipoles
is undergoing change and the tiny dipoles will be angularly accelerating,
either in magnitude or direction (precession). This realignment will
be accompanied by a net vortex flow of pressurized aether that passes
between neighbouring dipoles. This net flow of momentum is electromagnetic
radiation and it has a wave-like nature, in that the flow will constantly
be emerging from positrons and sinking into electrons. The average
speed of this flow is what determines the speed of light.
L4
- Galilean Invariance and Mach's Principle
Abstract.
Galileo's
«Principle of Relativity» omits any consideration
of an absolute frame of reference with respect to which
motion is measured. Kinetic energy would appear to be a relative
quantity whose magnitude depends on the chosen frame of reference,
or in the case of its centrifugal force derivative, depends
on which polar origin is chosen. The magnitude of any physical
interaction involving two bodies is only ever dependent on their
relative velocity, and there seems to be no way of exposing the existence
of any special frame of reference with respect to which linear kinetic
energy is an absolute physical quantity. The fact of centrifugal
force however does indicate that such a frame of reference must
exist, and that this frame appears to be embedded in a medium that
is in a state of zero rotation relative to the fixed background
stars. Rotation relative to the fixed background stars induces
centrifugal force, which suggests that kinetic energy is indeed
an absolute physical quantity that is induced by the interaction
of a moving body with a physical medium which pervades all of space.
In this article it will be proposed that the physical medium for the
propagation of light is also the cause of kinetic energy and centrifugal
force, and we will be reminded that Maxwell's equations are formulated
specifically with this medium as the standard of rest. Important
questions relating to the motion of this luminiferous medium
relative to the planets and the stars will then be discussed.
M4
- The Electron-Positron Sea
Abstract.
It is proposed that all space
is permeated with a dense electrically neutral sea of
electrons and positrons which serves as the medium for the
propagation of light. The challenge remains to devise a stable
bonding mechanism within this luminiferous medium that conforms
with Maxwell's equations by providing the necessary solidity
and the physical mechanism that will give rise to the characteristics
of electromagnetic waves, while at the same time allowing for
the fluidity that would avoid the problem of friction in the planetary
orbits.
M4'
- The Electron-Positron Sea
(A slightly revised
version of the previous paper - October
2017)
N4 -
Newton's Cradle Disproves Einstein's Theories of Relativity
Abstract.
The counter intuitive behaviour
of the Newton's Cradle is not, as is generally believed,
adequately explained in the literature. In particular, two
important issues are overlooked. One of these is that the elasticity
of the balls arises due to the fact that the balls are made
of hard material that doesn't easily deform during the collisions,
when in fact we might have expected the hard material to have actually
reduced the elasticity. This therefore rules out linear elasticity
and Hooke's law as being the principle action, and so it is proposed
that the energy waves that transfer the kinetic energy through
the row of balls are based on fine-grained rotational elasticity,
similar in nature to that which arises in electromagnetic radiation.
The other overlooked issue is that the kinetic energy waves that
move through the metal balls immediately after a collision, move
either to the right or to the left of the point of impact, or in both
directions, but since energy transfer inside the balls has an absolute
motion relative to the balls themselves, then whether the energy
within the balls moves to the right, or to the left, or in both
directions, must depend on the absolute motion of the balls. The direction
of the energy transfer within the balls cannot depend on an arbitrary
choice of rest frame. It therefore remains to determine the physical
basis for absolute motion and kinetic energy. Only then, in terms of
absolute motion, can the Newton's cradle be correctly analyzed.
O4 - Magnetic
Repulsion and the Gyroscopic Force
Abstract.
The counterintuitive gravity
defying behaviour that is exhibited by a pivoted gyroscope
suggests the involvement of an active spin-induced force,
similar in nature to the magnetic force, F = qv×B,
and which cannot be predicted by Newtonian mechanics. The
phenomenon of gyroscopic stability exhibits a strong reactance
which cannot be accounted for by the moment of inertia. The
physical connection between the inertial forces and magnetic repulsion
will be investigated.
O4'
- Magnetic Repulsion and the Gyroscopic Force
New revised version: 10th October
2015
This paper has been amended:
"The essence of the change is that I have now firmly concluded
that the inertial forces arise directly from Newton's laws
of motion and not as supplements. Polar coordinates exposes the
inertial forces in an inertial frame of reference". Here it is the
new abstract:
The counterintuitive gravity defying
behaviour that is exhibited by a pivoted gyroscope suggests
the involvement of an active spin-induced force, similar
in nature to the magnetic force, F = qv×B.
The phenomenon of gyroscopic stability exhibits a strong spin-induced
reactance which cannot be accounted for by the moment of
inertia alone. The physical connection between the inertial
forces and magnetic repulsion will be investigated.
P4 -
Centrifugal Force and the Electron-Positron
Sea
Abstract.
We often hear it said that centrifugal
force is not a real force and that it is only the effects
of inertia that are caused by a body undergoing its uniform
straight line path, as per Newton's first law of motion. These
effects of inertia however are very real and this suggests
that the inertial path itself must have an underlying physical
cause. This cause will now be ascribed to a background elasticity
that is rooted in electrostatics. The electric dipole, with
its inverse cube law field, will be proposed as the primary physical
cause of centrifugal force, while the inertial path and the
Mach Principle will be seen to result from the compound effect
of a dense multitude of superimposed dipole fields filling all
of space.
Q4
- Wikipedia and Centrifugal Force
Abstract.
Wikipedia is the on-line encyclopaedia
that anybody can edit. The content changes on a continual
basis. One of the rules is that editors must not insert original
research. The contents must reflect what is stated in reliable
sources. In the case of the centrifugal force article
however, reliable sources don’t always agree, and over the years,
the inability of editors at that article to consider the totality
of existing knowledge on the subject has led to never ending discussions
and edit wars. An example of the confusion that surrounds this topic
can be found at this web link,
http://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/37968/centrifugal-force-and-polar-coordinates
R4 -
Wikipedia and Coriolis Force
Abstract.
Wikipedia is the on-line encyclopaedia
that anybody can edit. The content changes on a daily
basis. One of the rules for editing is that editors must
not insert original research. The contents must reflect exactly
what is stated in reliable sources. Reliable sources present
Coriolis force as an artefact of making observations from
a rotating frame of reference. When stationary objects are viewed
from a rotating frame of reference, it's true that the effects are
unequivocally fictitious. However, in situations where an entire
system is rotating, the Coriolis force can be very real, and this fact
tends to cause confusion. It will be argued that in the former case
scenarios there is no Coriolis force present at all, real or fictitious,
while in the latter case scenarios the Coriolis force is due to
Newton's laws of motion, and that it already exists independently
of the rotating frame of reference.
S4
- The 1856 Weber-Kohlrausch Experiment (The Speed of Light)
(New revised version: 18.IV.2011)
Abstract.
Nineteenth century physicists Wilhelm Eduard Weber,
Gustav Kirchhoff, and James Clerk-Maxwell are all credited with
connecting electricity to the speed of light. Weber's breakthrough
in 1856, in conjunction with Rudolf Kohlrausch, revealed the speed
of light in the context of a ratio as between two different units of
electric charge. In 1857 Kirchhoff connected this ratio to the speed
of an electric signal travelling along a wire. Later, in 1862, Maxwell
connected this ratio to the elasticity in the all-pervading luminiferous
medium that serves as the carrier of light waves. This paper sets out
to establish the fundamental cause of the speed of light.
T4
- Compressed Orbits and the Secret Behind E = mc²
Abstract.
On the astronomical scale, the potential
energy in a closed orbit is due to the gravitational force
of attraction. These are uncompressed orbits. The gravitational
force is opposed by a centrifugal force acting internally from
within the system. This article will now consider the nature of the
potential energy in a system of multiple orbits that are pressing
against each other with centrifugal force while striving to dilate.
Centrifugal potential energy is shown to lie at the root of the famous
equation E = mc² .
U4
- Atomic Clocks and Gravitational Field Strength
Abstract.
A redefinition of potential energy better
emphasizes the physical reality of gravitational field strength.
The current definition only deals with motion on the large scale
and not with the fine-grained motions at molecular level which
are relevant to the mechanism of atomic clocks.
V4
- The Inertial Helicopter
Abstract.
A sea level object that is moving horizontally
at a speed greater than 8 km/sec is already in orbit and it
will rise upwards due to centrifugal force. Two such objects
tethered together while moving in opposite directions should therefore
spiral upwards like a helicopter. It will be proposed that the atom
is a dipole, and that it is the fundamental helicopter.
W4
- The Double Helix and the Electron-Positron Aether
(New revised version: 18.IV.2011)
Abstract.
This article takes a closer look at the bonding
and stability mechanisms within the electron-positron dipole
sea and how these result in the double helix theory of the magnetic
field. The physical connection between the inertial forces and
magnetic repulsion will be further investigated.
X4
- Electromagnetic Radiation in the Near Magnetic Field
Abstract.
This article follows on from previous papers
on the double helix theory of the magnetic field. A closer look
will be taken at the low energy electromagnetic radiation that
is confined to a solenoidal path along the field lines within
a near magnetic field, such as occurs in a transmission line pulse.
X4'
- Electromagnetic Radiation in the Near Magnetic Field
(A new revised
version of the previous paper: 16.I.2021)
Abstract.
This paper has now been updated following a realization
that, since flowing aether cannot pass laterally through itself,
then wireless EM radiation can only propagate beyond the near magnetic
field when the tiny vortices that fill all of space are in a state of
precession. This would only occur in the transient state, particularly
when the source current is AC
Y4
- Induction of Electrostatic Repulsion by Strong Gravity (The
Link between Gravity and Electromagnetism)
Abstract.
The radial lines of force that are associated
with Gauss's law indicate the presence of fluid-like sinks and
sources in matter, whether or not we know where these lead to.
This article will examine how two sinks can be either mutually attractive
or mutually repulsive depending on the rate of flow.
Z4
- The Pendulum and the Magnetic Connection
Abstract.
When analyzing pendulum motion, textbooks avoid
invoking centrifugal force. All upward acting forces are accounted
for by the tension in the rod. This tension must however be greater
in magnitude than gravity in order for a net upward force to be possible.
The role of centrifugal force in both the simple pendulum and the
conical pendulum will therefore be re-examined, and a connection
with magnetic repulsion will be suggested.
A5
- An Interpretation of Faraday's Lines of Force
Abstract.
The magnetic field is solenoidal, yet the Biot-Savart
Law which is the textbook equation for the magnetic field, indicates
the existence of a singularity owing to the fact that it involves
an inverse square law in distance. This dilemma is solved within the
context that an individual magnetic line of force constitutes a double
helix of sinks and sources closed on itself to form a toroidal ring
vortex.
- - - - -
4.X.2019:
With the following 7 last papers, F.D. Tombe concludes
his monumental work aiming to a comparison betewen classical
Maxwell electromagnetism and the (special) theory of relativity
introduced by Albert Einstein.
B5 - The Full
Significance of the Speed of Light
Abstract.
In the year 1855, German physicists Wilhelm Eduard
Weber and Rudolf Kohlrausch performed a landmark experiment of
profound significance. By discharging a Leyden jar (a capacitor), they
linked the speed of light to the ratio between electrostatic and
electrodynamic units of charge. This experiment was electromagnetism's
Rosetta Stone because the result can be used to, (i) identify the speed
of light as the speed of circulation of electric current, (ii) identify
the speed of light as the speed of electromagnetic waves through a
dielectric solid that pervades all of space, while noting that inertial
centrifugal force and dipole fields share in common an inverse cube law
in distance. The result can also be used to, (iii) identify magnetic
repulsion as a centrifugal force, and hence to establish the double helix
pattern that characterizes magnetic lines of force.
C5 - Straight
Line Motion
Abstract.
The straight line inertial path will be examined
from the perspective that it is caused by pressure equilibrium
in a sea of tiny aethereal whirlpools that are pressing against each
other with centrifugal force while striving to dilate. This is opposite
to the traditional perspective whereby centrifugal force is considered
to be a consequence of the tendency of a body to move in uniform
straight line motion in the absence of any Newtonian forces.
D5 - Faraday's
Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Abstract.
It will be shown how the magnetic vector potential,
A, is a momentum which is central to Faraday's law of
electromagnetic induction, and how the convective electromagnetic
force E = v×B is the factor which enables the
total time derivative to be used in Faraday's law.
E5
- The Significance of the Inertial Forces in Electromagnetism
Abstract.
The centrifugal force and the Coriolis force will
be described. There is a controversy over whether these forces
are real or fictitious. This controversy will be examined in conjunction
with its significance to electromagnetism.
F5 - Isotropy
in the Electromagnetic Field
Abstract.
In Part III of his 1861 paper On Physical Lines
of Force, James Clerk Maxwell introduces the concept of displacement
current in connection with the elasticity of the medium for the
propagation of light. During the course of Part III, the luminiferous
medium changes from an anisotropic sea of molecular vortices into
an isotropic dielectric solid. An attempt will be made to reconcile
these two seemingly contradictory mediums.
G5 - Cable Telegraphy
and Poynting's Theorem
Abstract.
Wireless EM radiation relates to magnetization while
the waves that travel alongside the conducting wires in transmission
lines relate to linear polarization. This article will examine how
these two phenomena may or may not be treated using the same basic
electromagnetic wave equations.
G5' - Cable
Telegraphy and Poynting's Theorem
(A new revised version of the previous paper:
14.II.2020)
Abstract.
Wireless EM radiation relates to magnetization
while the magnetic fields that travel alongside the conducting
wires in transmission lines are commonly associated with capacitance
and linear polarization. This article will examine how these two phenomena
may or may not be treated using the same basic electromagnetic wave
equations.
G5'' - Cable
Telegraphy and Poynting's Theorem
(A new revised version of the previous paper:
7.I.2021)
"I have been looking again at the differences
and similarities between wireless EM radiation and transmission
line pulses, and I finally came to the conclusion that the Poynting
Vector, ExH, does indeed apply in both cases, but of
course with the Faraday E in the wireless case and the Coulomb
E in the cable case. Previously, I had wrongly argued that it
only holds in the wireless case, and I based that argument on the fact
that Poynting's theorem hinges on Faraday's law. However, it suddenly
dawned on me that the Poynting vector itself doesn't necessarily hinge
on Poynting's theorem and that Poynting's theorem merely only applies
to time varying-electromagnetic induction. Transmission line pulses are
however convective phenomena, and just because Poynting's theorem doesn't
apply, doesn't mean that we can't have a Poynting vector telling us the
rate of energy flow in a transmission line pulse".
Abstract.
Wireless EM radiation relates to magnetization while
the electrostatic and magnetic fields that travel alongside the
conducting wires in transmission lines are associated with capacitance
and linear polarization. This article will examine how these two
phenomena may or may not be treated using the same electromagnetic
wave equations.
H5 - Radiation
Pressure and E = mc2
Abstract.
To show that the equation E = mc2 was
already implicit in Maxwell's 1861 paper On Physical Lines of
Force and that it doesn't mean that mass is equivalent to energy,
but rather it relates to the propagation of electromagnetic radiation
through an elastic solid.
I5
- Einstein's Big Mistake
From the Introduction:
Einstein overlooked the fact that the speed of light,
as it occurs in the Lorentz transformation equations, is determined
by the density and elasticity of a physical medium which pervades
all of space, and which acts as the medium for the propagation of light
waves. This fact had already been established by Scottish physicist
James Clerk Maxwell, (1831-1879), who happened to die in the same year
that Einstein was born. The physical medium in question was known to
Maxwell as the luminiferous medium although Einstein later referred
to it as a Lichtäthers (luminiferous aether). Maxwell provided us
with a reasonably clear picture of what the physical structure of this medium
would need to be. He proposed that all of space is filled with a sea of molecular
vortices comprised of tiny aethereal whirlpools, each surrounded by electric
particles. This was an idea, which according to Tesla in 1907, had in essence,
long been known to men of old.
14.V.2021: A new paper,
"in response to issues arising on a discussion thread".
J5
- Aether Friction in the Planetary Orbits
Abstract.
When a theory of electromagnetism promotes the idea that
the medium for the propagation of light waves is an elastic solid
comprised of electric particles, the question is always going to be
asked as to why this medium would not generate friction in the planetary
orbits, such as would cause the planets to spiral into the Sun. It would
be impossible for a moving body to completely avoid any physical interaction
with these electric particles, and so, in order to comply with Kepler's
Laws of Planetary Motion, this interaction must be the actual cause of
the inertial forces, as opposed to being the cause of any dissipative
friction.
J5'
- Aether Friction in the Planetary Orbits
(A new revised version of the previous paper:
21.IX.2021)
"I have made some amendments to this article. The essence
of the changes is mainly to emphasize the fact that entrainment of
the luminiferous medium by gravity is necessary in order for centrifugal
force to be an actual physical repulsion. This was implied in the
original version, but now it is emphasized".
21.IX.2021: "Despite having intended
in 2019 to stop writing physics articles, I continued to be involved
in discussion threads. Answering questions caused me to come up with
new ideas as well as better ways to express my older ideas. As such
I ended up writing more articles. It is still nevertheless my intention
to move on to other interests in the near future".
K5
- Centrifugal Force in the Schwarzschild Field
"An attempt to reconcile General Relativity with aether
theory. The presence of the aether as an absolute standard of rest,
removes the paradoxes from STR".
Abstract.
Centrifugal force is an inertial effect which is induced
by motion through the Minkowski 4D space-time continuum. While it
can act in opposition to gravity, there is evidence from Einstein's
General Theory of Relativity, that gravity, if strong enough, can affect
the physical structure of the 4D space-time continuum in such a way as
to destroy the centrifugal force and convert it into an electrostatic
force of attraction that augments the gravity. The physical nature of centrifugal
force and the manner in which it can be altered by gravity will now be
investigated.
L5
- The Physical Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
"I wrote the attached paper in order to show readers
Maxwell's derivation of the electromagnetic wave equation in his
1873 Treatise. The paper works through the derivation with a link
supplied to the 1873 paper, and my summary uses modern vector notation
and SI units".
Abstract.
Since Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell wrote his Treatise
in 1873, it has generally been believed that wireless electromagnetic
radiation consists of sinusoidally oscillating electric and magnetic
fields, perpendicular to each other and mutually perpendicular to the
direction of propagation. The reasons as to why Maxwell concluded these
mutually perpendicular orientations will now be investigated, as will
the issue of the relative phase in time as between these electric
and magnetic disturbances.
M5 - The
Apparent Dual Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
Abstract.
The Planck-Einstein relation, E = hf, relates the energy of
discrete pulses of black body radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays to
their wave frequency. This relationship appears to contradict the wave
theory of light. An investigation will now take place regarding whether
the Planck-Einstein relation, and Planck's constant itself, lie in the
domain of the medium for the propagation of light, or in the vestibule
of the atom, or in both.
N5
- The Positronium Orbit in the Electron-Positron Sea
Abstract.
The purpose is to show that the equation E = mc2
was already implicit in Maxwell's 1861 paper "On Physical Lines of
Force" and that it doesn't mean that mass is equivalent to energy, but
rather it relates to the propagation of electromagnetic radiation through
a sea of rotating electron-positron dipoles which pervades all of space.
O5-
The Double Helix Theory of the Magnetic Field
(A "very much refined version" of
the previous paper A,
and successive revisions)
Abstract.
The historical linkage between optics and electromagnetism can
be traced back to the year 1855, when Wilhelm Eduard Weber and Rudolf
Kohlrausch, by discharging a Leyden Jar (a capacitor), demonstrated
that the ratio of the electrostatic and electrodynamic units of charge
is equal to c√2, where c is the directly measured speed of light. Although
not initially aware of the connection to the speed of light, Weber interpreted
c√2 as a kind of mutual escape velocity for two elements of electricity
in relative motion, such as would enable the induced magnetic force to
overcome the mutual electrostatic force. A few years later, James Clerk
Maxwell converted this ratio from electrodynamic units to electromagnetic
units, hence exposing the speed of light directly. On connecting Weber’s
ratio to the dielectric constant in an all-pervading elastic solid, Maxwell
concluded that light consists in the transverse undulations of the same
medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena. The differing
perspectives of Weber and Maxwell can be reconciled by linking the speed
of light to the circumferential speed of the electric particles surrounding
the tiny molecular vortices that Maxwell believed to be the constituent
units of the luminiferous medium. If we consider these molecular vortices
to be tiny electric current circulations, mutually aligned along their
rotation axes to form magnetic lines of force, magnetic repulsion can
then be explained in terms of centrifugal pressure acting sideways from
these field lines. And if these molecular vortices should take the more
precise dipolar form of an electron and a positron in mutual orbit, we can
then further explain magnetic attraction, this time in terms of the more
fundamental electrostatic force being channeled along the double helix of
electrons and positrons that forms a magnetic line of force.
P5
- The Lorentz Aether Theory
Abstract.
The Lorentz transformations are best known for the relativistic
Lorentz factor, 1/√(1 – v2/c2), which appears
in the equations of special relativity. It is also known that the Lorentz
transformations can be used to derive the Biot-Savart law in the form
B = μ0ε0v×E and also the Maxwell-Lorentz
force in the form E = v×B.
What is not well-known however is that the emergence of these
two cross-product equations has got no bearing on the Lorentz factor
itself. It is often argued that the magnetic force E = v×B
is a relativistic effect, yet it clearly isn't. While the connection
between the Lorentz transformations and the return-path Doppler effect
in light is a matter of interest, this article will take a closer look
at the classical origins of the two vector cross-product equations that
emerge from the Lorentz transformations alongside the Lorentz factor,
but independently of it.
P5
' - The Lorentz Aether Theory
(A new
revised version of the previous paper: 18.IV.2023)
Abstract.
The Lorentz transformations are best known for the relativistic
Lorentz factor, γ = 1/√(1 – v2/c2), which appears
in the equations of special relativity, and it is also known that the Lorentz
transformations can be used to derive both the Biot-Savart law in the form
B = (v×E)/c2, and the magnetic force in
the form E = v×B.
What is not so well-known, however, is that the Lorentz factor itself
plays no role in the emergence of these two equations. Nevertheless, it is
often wrongly argued that magnetism is a relativistic effect, despite the
very obvious fact that magnetism is observable at laboratory speeds. This
article will now examine the role that the physical structure of the luminiferous
medium plays in the existence of magnetism.
15th June 2023 - A new abstract for this paper:
Abstract.
The Lorentz transformations are best known for the relativistic
Lorentz factor, γ = 1/√(1 – v2/c2), which appears
in the equations of special relativity, and it is also known that the Lorentz
transformations can be used to derive both the Biot-Savart law in the form
B = (v×E)/c2, and the magnetic force in
the form E = v×B.
It could therefore be argued that magnetism is a relativistic effect,
even though it is observed at laboratory speeds. This article will now examine
how the physical structure of the luminiferous medium enables the existence
of magnetism. The aim will be to identify the latent presence of the speed
of light within the fabric of a laboratory magnetic field. On establishing
this, the Lorentz factor will then be exposed as an asymptotic coefficient
which only becomes significant at speeds close to the speed of light.
Q5
- The Rattleback and the Magnus Force
Abstract.
The rattleback (Celtic stone) is the most mysterious
phenomenon in classical mechanics. It freely undergoes a complete reversal
of its angular momentum without the involvement of any apparent external
torque. This mystery will now be investigated at the atomic and molecular
level.
R5
- The Absolute Direction of Alternating Current
Electric energy that is generated at a power station flows
in one direction only, away from the station and to the consumer, yet
the electric current itself alternates to-and-fro. How can this be possible?
We will seek to solve this mystery.
R5'
- The Absolute Direction of Alternating Current
(A new revised
version of the previous paper: 9.IX.2022)
"I've amended the attached paper to emphasize the
fact that the circulatory motion in each AC cycle is of a caterpillar track
nature, as opposed to a slipping wheel nature".
Abstract.
The Mystery - Electric energy that is generated at a power station
flows in one direction only, away from the station and to the consumer,
yet, at both the generator end and at the consumer end, the electric current
itself alternates to-and-fro. How can this be possible? We will now take
a closer look at the transient state that arises in an electric circuit
during the first moments after the power is connected, or after each moment
of direction reversal in the case of AC. It’s only in the transient state
that transmission occurs, whether it be wireless transmission or cable
transmission.
S5
- The Commonality between Light and Electric Current
Abstract.
In the year 1855, German physicists Wilhelm Eduard Weber and
Rudolf Hermann Arndt Kohlrausch performed an experiment involving the
discharge of a Leyden jar and they established the ratio between electrostatic
and electrodynamic units of charge. This ratio, which became known as Weber's
constant, was measured numerically to be c√2, where c was very close to the
speed of light. Since this experiment had nothing to do with optics, the
question then arises as to whether they had perhaps actually measured the
speed of electric current, which just happens to be close to the speed of
light for the reason that the speed of light is in turn determined by the
speed of electric current within the context of the medium for the propagation
of light. We must establish the physical commonality between light and electric
current.
S5'
- The Commonality between Light and Electric Current
A new revised version of the
previous paper (23.X.2022)
"On further research, I realized that Kirchhoff
never actually derived the Telegraphers' equations. He came close to
it, but didn't derive the ones that Heaviside later derived. He did however
identify the Weber constant with the speed of light. As such, I have made an amendment in the paper".
Abstract.
Hermann Arndt Kohlrausch performed an experiment involving the
discharge of a Leyden jar and they established the ratio between electrostatic
and electrodynamic units of charge. This ratio, which became known as Weber's
constant, was measured numerically to be c√2, where c was very close to the
speed of light. Since this experiment had nothing to do with optics, the question
then arises as to whether they had perhaps actually measured the speed of
electric current, which just happens to be close to the speed of light for
the reason that the speed of light is in turn determined by the speed of
electric current within the context of the medium for the propagation of
light.
We must establish the physical commonality between light and electric current.
T5
- The Deeper Physical Nature of Electric Current
Abstract.
While it is generally accepted that electric current involves the
motion of electric charge through conducting channels, there is observable
evidence in the field of pulse transmission, that electric current exhibits
wave-like behaviour, and that two electric pulses can pass right through
each other in opposite directions along the same wire. An attempt will
be made to reconcile these two seemingly contradictory natures of electric
current.
U5
- Tesla on the Aether and the Implications
"I decided to draw closer attention to what Tesla said about the
aether and then show a derivation of the EM wave equation in the vector
A (magnetic vector potential) that can be directly linked to the concept".
Abstract.
Serbian American electrical engineer Nikola Tesla (1856-1943), wrote:
"Long ago he (mankind) recognized that all perceptible matter comes from
a primary substance, of a tenuity beyond conception, filling all space,
the Akasha or luminiferous ether, which is acted upon by the life-giving
Prana or creative force, calling into existence, in never ending cycles,
all things and phenomena. The primary substance, thrown into infinitesimal
whirls of prodigious velocity, becomes gross matter; the force subsiding,
the motion ceases and matter disappears, reverting to the primary substance".
We will now investigate what exactly this was supposed to mean.
V5
- Summary Article - Electromagnetism and Optics
"It's still my intention to move to other fields of interest, but
I decided that before I completely finish with the physics, I would do a
summary paper in the form of a historical chronology of all the important
events in the unification of light and electric current. It begins with the
1855 Weber-Kohlrausch experiment."
Abstract.
A chronology of the main events in the history of the unity of optics
and electromagnetism.
V5'
- Electromagnetism and Optics – Historical Chronology
A chronology of the main events in the history of the unity of
optics and electromagnetism.
(A new revised version of the previous paper:
17.XI.2023)
"I did some re-wording in the 1889-1908
section of the summary paper, and I also changed the title. The re-wording
was aimed at clarifying the fact that the space and time variables in the
Lorentz transformation should be connected to the circumference and angular
period of the relevant atoms in the context under consideration".
___________________________________________________________________________

